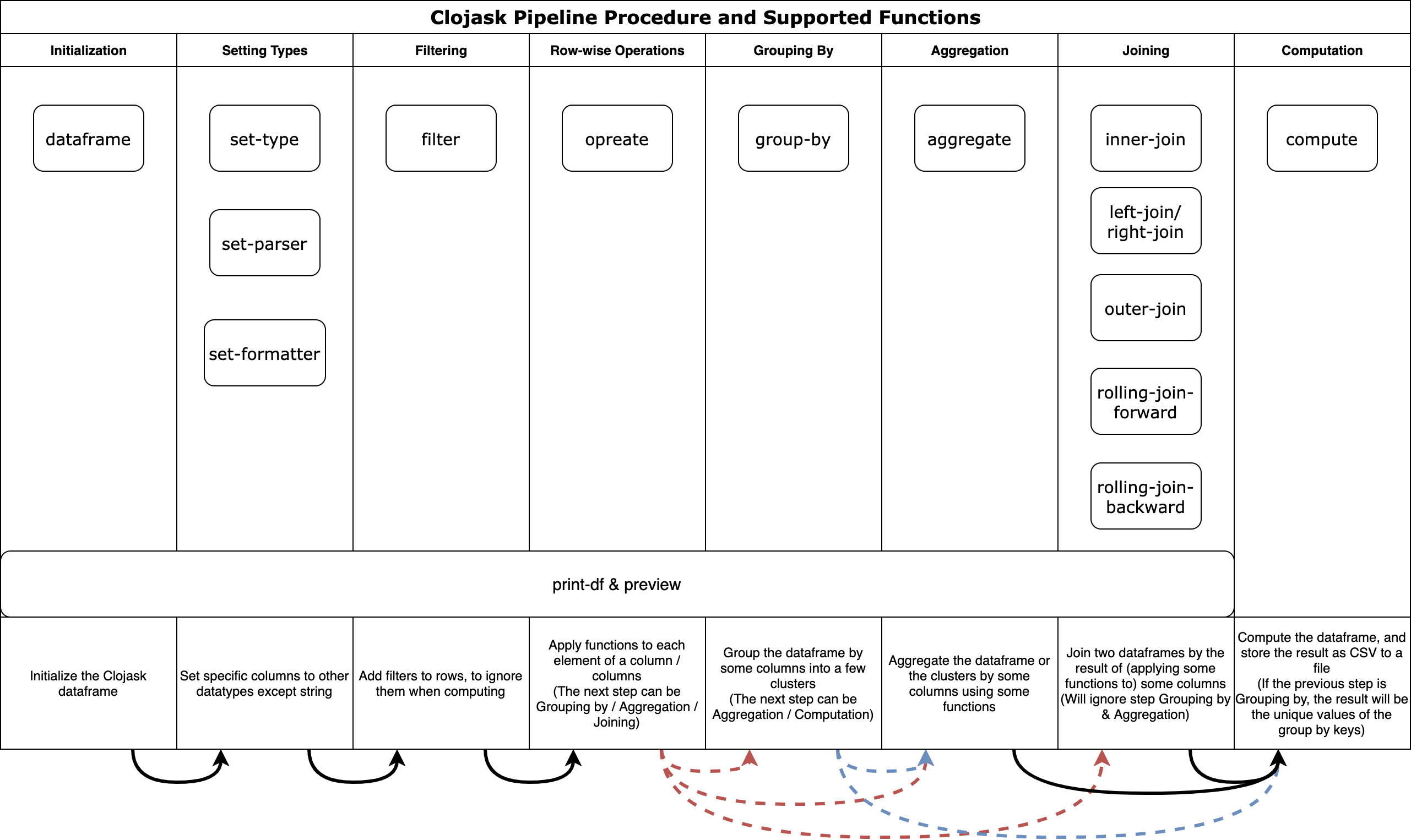
API Docs
- Basic Information
- dataframe
- print-df
- preview
- get-col-names
- rename-col
- filter
- set-type
- set-parser
- set-formatter
- operate (In-place modification)
- operate (Column generating)
- group-by
- aggregate
- sort (
Deprecated ) - inner-join / left-join / right-join / outer-join
- rolling-join-forward / rolling-join-backward
- compute
See also extensions for more native Clojask functions.
Basic Information
The APIs below are defined in namespace
clojask.dataframe.Most dataframe manipulation operations are performed lazily (except for
sortandjoin). They will be executed all at once whencomputeis called.By default (except for Excel input), all columns are assigned with the data type
stringwhen the dataframe is initialized.[ ] surrounding the argument indicates an optional operation.
Without further specification, the return of all these functions is the resultant Clojask dataframe with type
clojask.dataframe.classes.DataFrame. Therefore, you can pipeline these functions with->macros.(-> (dataframe "xxx.csv") (set-type "Colx" "int") (operate inc "Colx") ... (compute 8 "xxx-modified.csv"))
dataframe
Defines the dataframe and returns clojask.dataframe.classes.DataFrame
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
input-directoryor input-function | String Function | Path of dataset file Source of the dataset | If input-directory, the output format is automatically set to correspond to the input format (can be modified by :output option during compute) and (coming soon) progress indication is available during compute.If input-function comes from (fn [] (clojask-io.input.read-file ... :size true :output true)), the above functions are also supported.If input-function is user-defined, the above functions are not available, but you can still change the output format by :output option of compute laterHow to define input-function? The input-function should be a function that returns lazy sequence of vectors that represents each row. "Lazy" here is necessary if the dataset is larger than memory. |
[if-header] | Boolean | If the dataset has column names as the first row | If false, the default column names will be $Col_i$, where $1\leq i\leq number \space of \space columns$. |
;; defines df as a dataframe from dataframe.csv file
(def df (dataframe "resources/Employee.csv"))
;; define df to be a dataframe with customized seperator
(require '[clojask-io.input :as input])
(def df (dataframe (fn [] (input/read-file "resources/Employees.csv" :sep "," :output true :stat true))))
;; define df with a lazy sequence
(def df (dataframe (fn [] (map vector (take 1000 (iterate inc 1)) (take 1000 (repeat 1)))) :if-header false))
print-df
Provides a preview of the resulting data (column headings, datatype, and data) by performing a sample based compute on the current dataframe manipulation operations to be performed by compute. Print the result to the nice-formatted table.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
[sample size] | Integer | Specify the sample size taken from the beginning of the dataframe | Default of 1000 elements |
[return size] | Integer | Specify the returning size of the dataframe elements | Default of 10 elements |
(print-df x 1000 10)
;; prints 10 rows of data based on 1000 sample data entries with the current operations
preview
Provides a preview of the resulting data (column headings, datatype, and data) by performing a sample based compute on the current dataframe manipulation operations to be performed by compute. Return the result as a vector of maps.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
sample size | Integer | Specify the sample size taken from the beginning of the dataframe | Default of 1000 elements |
return size | Integer | Specify the returning size of the dataframe elements | Default of 10 elements |
[formatting] | Boolean | Whether to format the results to string using the formatters defined by set-type and set-formatter | By default, false, i.e. values are kept as their last data type before formatting |
(preview x 1000 10)
;; [{"Employee" "1" "EmployeeName" "Alice" "Department" "11" "Salary" "300"} {...} ...]
get-col-names
Get the column names of the dataframe
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object |
Return
get-col-names returns a clojure.lang.PersistentVector
(get-col-names x)
;; columns: ["Employee" "EmployeeName" "Department" "Salary"]
rename-col
Rename the column names in the dataframe
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
old column | String | The old column name | Should be an existing column name in dataframe |
new column | String | The new column name | Should be a unique column name from the existing ones |
;; columns: ["Employee" "EmployeeName" "Department" "Salary"]
(rename-col x "Department" "new-Department")
filter
Filter the dataframe by rows.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
columns | String / collection of strings | The columns that the predicate function would apply to | |
predicate | Function | The predicate function to determine if a row should be kept | This function should have the same number of arguments with the above columns and in the same order. Only rows that return true will be kept. |
Example
(filter x "Salary" (fn [salary] (<= salary 800)))
;; this statement deletes all the rows that have a salary larger than 800
(filter x ["Salary" "Department"] (fn [salary dept] (and (<= salary 800) (= dept "computer science"))))
;; keeps only people from computer science department with salary not larger than 800
set-type
Set the data type of a column. As a result, the value will be parsed as the assigned data type when it is used in any subsequent operations.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
column | String | Target columns | Should be existing columns within the dataframe. |
type | String | Type of the column | The natively supported types are: int, double, string, date. Note that by default all the column types are string. If you need a special parsing function, see set-parser. |
Example
;; set data type of the column "Salary" to be double
(set-type x "Salary" "double")
set-parser
A more flexible way to set type by specifying the customized parser.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
column | String | Target columns | Should be existing columns within the dataframe |
parser | function | The parser function that will parse a string to other types (or even string) | The function should take only one argument which is a string, and the parsed type should be serializable. |
Example
;; parse all the values in "Salary" with this function
(set-parser x "Salary" #(Double/parseDouble %))
set-formatter
A more flexible way to set type by specifying the customized formatter.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
column | String | Target columns | Should be existing columns within the dataframe |
formatter | function | The formatter function that will format a data type (can be checked from the print-df function) to string for outputting | The function should take only one argument which is a string, and the parsed type should be serializable. |
Example
;; parse all the values in "Salary" with this function
(set-parser x "Salary" #(Double/parseDouble %))
operate (In-place modification)
In-place modification on a single column
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
operation | function | Function to be applied lazily | The function should take only one argument which is the value of the below column. |
column name | Keyword | Target columns | Should be existing columns within the dataframe. |
Example
;; set data type as double
(set-type x "Salary" "double")
;; take the negative of the column "Salary"
(operate x - "Salary")
operate (Column generating)
Calculate the result and store in a new column
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
operation | function | Function that is to be applied lazily | Argument number should align with the number of column names below, ie if operation functions takes two arguments, the length of column names should also be two, and in the same order that is passed to the function. |
column name(s) | String or collection of Strings | Target columns | Should be existing columns within the dataframe. |
new column | String | Resultant column | Should be new column(s) other than those existing in the dataframe. |
Example
(operate x str ["Employee" "EmployeeName"] "new")
;; concats the two columns into the "new" column
group-by
Group the dataframe by some specific columns (always used together with aggregate), or group the dataframe by function output(s)
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
groupby-keys | String / Collection | Group by columns (functions of columns) | Find the specification below . |
Example
;; group by one or more columns
(group-by x ["Department"])
(group-by x ["Department" "DepartmentName"])
Group-by Keys Specification
Group-by Functions Specification
- Take one argument
- Return type: int / double / string
Pair group-by functions with group-by keys
One general rule is to put the group-by function and its corresponding column name together.
Examples
(defn rem10
"Get the reminder of the num by 10"
[num]
(rem num 10))
(group-by x [rem10 "Salary"])
;; or
(group-by x [[rem10 "Salary"]])
If no group-by function, the column name can be alone.
(group-by x "Salary")
;; or
(group-by x ["Salary"])
You can also group by the combination of keys. (Use the above two rules together)
(group-by x [[rem10 "Salary"] "Department"])
;; or
(group-by x [[rem10 "Salary"] ["Department"]])
aggregate
Aggregate the dataframe(s) by applying some functions. The aggregation function will be applied to every column registered in sequence.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
aggregation function | function | Function to be applied to each column | Should take a collection as argument. And return one or a collection of predefined type*. |
column name(s) | String or collection of String | Aggregate columns | Should be existing columns within the dataframe |
[new column] | String or collection of string | Resultant column | Should be new columns not in the dataframe |
Example
(require '[clojask.api.gb-aggregate :as gb-agg])
(require '[clojask.api.aggregate :as agg])
;; aggregate without group, apply aggregation to the whole dataframe
(aggregate x agg/max "Salary")
(group-by x "Department")
;; get the max/min of the selected column(s) of each group
(aggregate x gb-agg/max ["Salary"] ["Salary-max"])
(aggregate x gb-agg/min ["Employee" "EmployeeName"] ["Employee-min" "EmployeeName-min"])
Custom functions can be made for aggregation. Please refer to Aggregation Function API for additional details
The keys used in specifying the aggregate operation are identical to the group-by function
sort (Deprecated )
Immediately sort the dataframe
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
trending list | Collection (seq vector) | Indicates the sort order | Example: ["Salary" "+" "Employee" "-"] means that sort the Salary in ascending order, if equal sort then by Employee in descending order |
output-directory | String | The output path |
Example
;; sort by "Salary" in ascending order
(sort x ["+" "Salary"] "path/output.csv")
inner-join / left-join / right-join / outer-join
Inner / left / right join two dataframes on specific columns
Remarks:
The registered operations and filters (like compute) will be automatically pipelined. You could think of join as as an operation that first computes the two dataframes then joins them together.
Only compute will be able to be performed after joing functions
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe a | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
dataframe b | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
a join keys | String / Collection | The keys of a to be aligned | Find the specification here |
b join keys | String / Collection | The keys of b to be aligned | Find the specification here |
[column prefix] | Collection of strings | Add to the front of the two column names | For example, ["a" "b"], and the resultant dataframe will have headers "a_xxx" and "b_xxx" respectively |
Example
(def x (dataframe "path/to/a"))
(def y (dataframe "path/to/b"))
(def z (inner-join x y ["col a 1" "col a 2"] ["col b 1" "col b 2"]))
(compute z 8 "path/to/output")
;; inner join x and y
(def z (left-join x y ["col a 1" "col a 2"] ["col b 1" "col b 2"]))
(compute z 8 "path/to/output")
;; left join x and y
(def z (right-join x y ["col a 1" "col a 2"] ["col b 1" "col b 2"]))
(compute z 8 "path/to/output")
;; right join x and y
Return
A Clojask.JoinedDataFrame
Unlike clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame, it only supports three operations:
print-dfget-col-namescompute
This means you cannot further apply complicated operations to a joined dataframe. An alternative is to first compute the result, then read it in as a new dataframe.
rolling-join-forward / rolling-join-backward
Rolling join two dataframes on columns. Forward will find the largest of the smaller in b while backward, while backward find the smallest of the larger in b.
You can refer to here for more details about rolling joins.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe a | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
dataframe b | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame | The operated object | |
a join keys | String / Collection | The column names of a to be aligned | Find the specification here |
b join keys | String / Collection | The column names of b to be aligned | Find the specification here |
a roll key | String | The column name of a to be aligned | Will be compared with b roll key using function compare |
b roll key | String | The column name of b to be aligned | Will be compared with a roll key using function compare |
[column prefix] | Collection of strings | Add to the front of the two column names | For example, ["a" "b"], and the resultant dataframe will have headers "a_xxx" and "b_xxx" respectively |
[limit] | Function (two arguments) | Another a condition checking before actually joining the two rows | For example, sometimes we want to discard the join when the time gap between two rows are too large. So we can let this compare function return false to stop joining. |
Example
(def x (dataframe "path/to/a"))
(def y (dataframe "path/to/b"))
(rolling-join-forward x y ["Employee"] ["Employee"] "Salary" "Salary")
(rolling-join-forward x y ["Employee"] ["Employee"] "Salary" "Salary" :limit (fn [a b] (if (> (- a b) 10) false true)))
;; if the salary of a - b exceeds 10, we will not join the two rows
Return (Same as inner-join)
A Clojask.JoinedDataFrame
Unlike clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame, it only supports three operations:
print-dfget-col-namescompute
This means you cannot further apply complicated operations to a joined dataframe. If you need so, an alternative is to first compute, then read the result in as a new dataframe.
compute
Compute the result. The pre-defined lazy operations will be executed in pipeline, ie the result of the previous operation becomes the argument of the next operation.
| Argument | Type | Function | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
dataframe | clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame / Clojask.JoinedDataFrame | The operated object | |
num of workers | int (max 8) | The number of worker instances (except the input and output nodes) | Uses Onyx as the distributed platform |
output path | String / nil | The path of the output csv file | If the path already exists, will overwrite the file. If nil, will store the output in memory as a vector of vectors, which represent each row. See example. |
[exception] | Boolean | Whether an exception during calculation will cause termination | By default false. Is useful for debugging or detecting empty fields |
[order] | Boolean | If enforce the order of rows in the output to be the same as input | By default false. If set to true, will sacrifice the performance. |
[output-function] | Function | Specify how to output a row vector to the output file | Takes two arguments.writer java.io.BufferedWriterrows clojure.lang.PersistentVector (rows) of clojure.lang.PersistentVector (each row) |
[select] | String / Collection of strings | Chooses columns to select for the operation | Can only specify either of select and exclude |
[exclude] | String / Collection of strings | Chooses columns to be excluded for the operation | Can only specify either of select and exclude |
[header] | Collection of strings | The column names in the output file that appears in the first row | Will replace the default column names. Should be equal to the number of columns. |
[melt] | Function (one argument) | Reorganize each resultant row | Should take each row as a collection and return a collection of collections (This API is used in the extensions.reshpae.melt) |
[in-memory] | Boolean | Whether the computation should all be completed in memory | If set to true, this affects the computation procedure of groupby-aggregation and joins. These operations originally will write to and read from intermediate group files in disk. Now it will stores these groups in memory only, which will speed up the computation process. However, when the dataframe is larger than memory, this option should not be set to false. Other operations are not affected because they natively do not require out-of-memory steps. |
Return
A clojask.classes.DataFrame.DataFrame, which is the resultant dataframe. / A vector of vectors, which represent each row, if output path = nil.
Example
(compute x 8 "output.csv" :exception true)
;; computes all the pre-registered operations
(compute x 8 "output.csv" :select "col a")
;; only select column a
(compute x 8 "output.csv" :order true)
;; make sure the order of the output is the same of the input
(compute x 8 nil :in-memory true)
;; compute the dataframe in memory and store the dataframe also in memory
(compute x 8 "output.csv" :select ["col b" "col a"])
;; select two columns, column b and column a in order
(compute x 8 "output.csv" :exclude ["col b" "col a"])
;; select all columns except column b and column a, other columns are in order
(compute x 3 "output.csv" :output (fn [wtr rows] (doseq [row rows] (.write wtr (str (str/join ", " row) "\n")))))
;; seperate each value in the row with ", "; seperate each row by "\n"
(compute x 8 "output.csv" :melt (fn [row] (map concat (repeat (take 2 x)) (take-last 2 x))))
;; each result row becomes two rows
;; [a b c d] => [[a b c] [a b d]]